The Tesoro Eldorado Metal detector is considered as a powerful metal detector, it is able to detect a 25 mm coin at a depth of about 30 cm, and the maximum detection depth, according to the builder, is 1.5 meters. The detector can work both in the search mode for all metals, and with discrimination.
Technical characteristics of the Tesoro Eldorado Metal detector :
- The type of the device refers to induction-balance
- The operating frequency is 8-10 kHz
- There is a Pin-Point detection mode in statics
- The device is powered by 12V
- Operating mode - dynamic
- There is a sensitivity level control
- There is a threshold tone control
- There is also ground balance (manual)
- The current consumption without sound is approximately 30 mA.
Depth of detection depending on the size of the object:
- The visibility of the 25 mm coin is 30 cm
- The Golden Ring - 25 cm
- The depth of detection of the helmet is 100-120 cm;
- Maximum - 150 cm
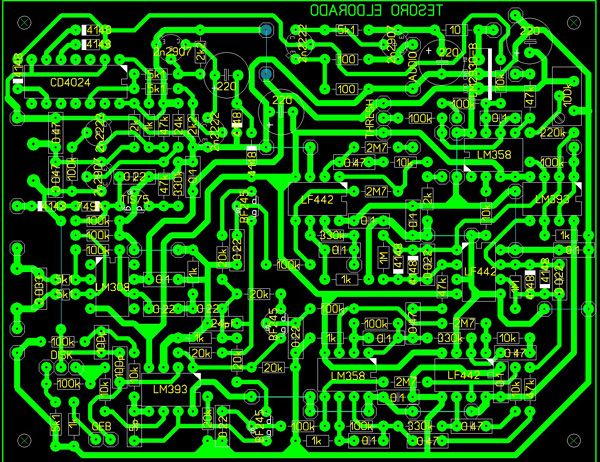
Schematic diagram:

THEMATIC TOOLS AND PARTS-LIST:
Components and tools needed for assembly are:
- soldering iron;
- enameled wire 0.27 mm;
- foil
- varnish;
- materials for creating a metal detector body and the coil;
A complete list of electronic components can be seen in the photo.

Metal detector manufacturing process:
Step one. Printed Circuit Board
As with all metal detectors, everything starts here at the heart of the device, namely the printed circuit board. The scheme here is rather complicated. Everything must be collected accurately and reliably, otherwise it will not be easy to find the place of the problem later.
It all starts with soldering the jumpers, then you can start installing the resistors.
Among other things, for assembling the board, the author recommends using a device that can determine the capacitance of capacitors. Due to the fact that the device has two identical amplification channels, all parts for assembly must be as identical as possible.

Step two. Assembling the coil DD
Since the designer has already prepared a case for a metal detector, at this step you can only see and understand how the coils work and what they should be.
The DD coil is made in the same way as for all balanced type metal detectors. The TX coil has 100 turns of 0.27mm wire and the RX coil has 106 turns.

When the coils are wound, they need to be wrapped with threads and soaked well with varnish. Further, when the varnish is dry, the coils should be tightly wrapped with electrical tape. Foil is used as a shielding, it must be wound around the entire coil, leaving a distance of 1 cm between the end and the beginning of the foil in order to avoid a short circuit.

The coil can also be shielded with graphite; for this, graphite is taken, mixed with nitro-lacquer in a 1: 1 ratio and applied to a 0.4 mm thick wire pre-wound without gaps on the coil. The wire connects to the cable shield.
Step three. The final stage of assembly
Now the coil can be installed with the body and by eye to bring the balance. As testing, you need a ferrite, there should be a double beep on it, and a single beep on the coin. If the opposite is true, the terminals of the receiving winding must be reversed.
The designer tunes each coil in frequency separately, while it is very important that there are no metal objects nearby. To tune the coils, a resonance meter is used. The attachment must be connected to the metal detector board in parallel with the transmitting coil and the frequency must be measured. By selecting a capacitor, you need to achieve a frequency 600 Hz higher than in TX.
When the resonance is selected, you need to assemble the coil and see if the device sees the VDI scale, starting from aluminum and ending with copper. If the entire scale on the device does not work, then you need to select the capacity of the resonant capacitor in the RX circuit in increments of 0.5-1 nF. As a result, the device should see the foil at the minimum discrimination, and copper at the maximum.

Finally, the coil is fixed with hot melt glue. To facilitate it, the designer seals all the voids with foam. It also needs to be placed on hot melt glue, otherwise it will float up after pouring. Well, then the whole thing is filled with epoxy.
Filling the first layer, you need to leave a distance of 2-3 mm from the top. Next, a second layer of resin with a color scheme is poured. Aniline dye, which is used for dyeing fabrics, is excellent as a color scheme. To mix the components, the dye must first be mixed with the hardener, and then the hardener must be mixed with the resin, otherwise the dye will not mix.
Finally, you can assemble the board and connect all the nodes. For testing, you need to connect the power and go through all the points where it should be.
Next, you need to check the discriminator. Turning the knob, all metals should be cut in turn, from aluminum to copper, but copper should not be cut. If everything works like this, then the device is assembled correctly. The scale must be made so that it fits completely into the radius of rotation of the discriminator knob, and this is done by selecting C10. If the capacitance of the capacitor is reduced, the jackal will stretch, if it is increased, then vice versa.
It is also worth saying a few words about the cable, the author has four cores. Two wires go to the transmitting coil and two to the receiving one, and the screen is connected to the body.









![[Arduino FreeRTOS tutorial] How to use semaphore and mutex](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEjv4nInC0gGae_exqVbGJ3vHTe70Mt_3Tc2OTotIjgVpf3BPNJnmGYrvEYBxF3gUiDNfJl5IHSd-2ShuRFe7cR5AtsimzD6NZtmfCz-NNV1rLmvK3mw1yGjlMYCthIAOm3lz_vY7CTygjfPdmdR6fWtLJomA46NJOD8HGVMzLPK2mF9I9eE3VsJbQI=w72-h72-p-k-no-nu)




No comments:
Comments